Imaging Cerebral Microhemorrhages in Military Service Members with Chronic Traumatic Brain Injury
By: Karen Holzberger, President & CEO of SpinTech MRI
Author(s): Wei Liu, DSc Karl Soderlund, MD Justin S. Senseney, MS David Joy, BS Ping-Hong Yeh, PhD John Ollinger, PhD Elyssa B. Sham, BA Tian Liu, PhD Yi Wang, PhD Terrence R. Oakes, PhD Gerard Riedy, MD, PhD
Journal: Radiology
Published: 2016
Read Full Paper: https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/radiol.2015150160?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%20%200pubmed
Abstract
Purpose
To detect cerebral microhemorrhages in military service members with chronic traumatic brain injury by using susceptibility-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. The longitudinal evolution of microhemorrhages was monitored in a subset of patients by using quantitative susceptibility mapping.
Method
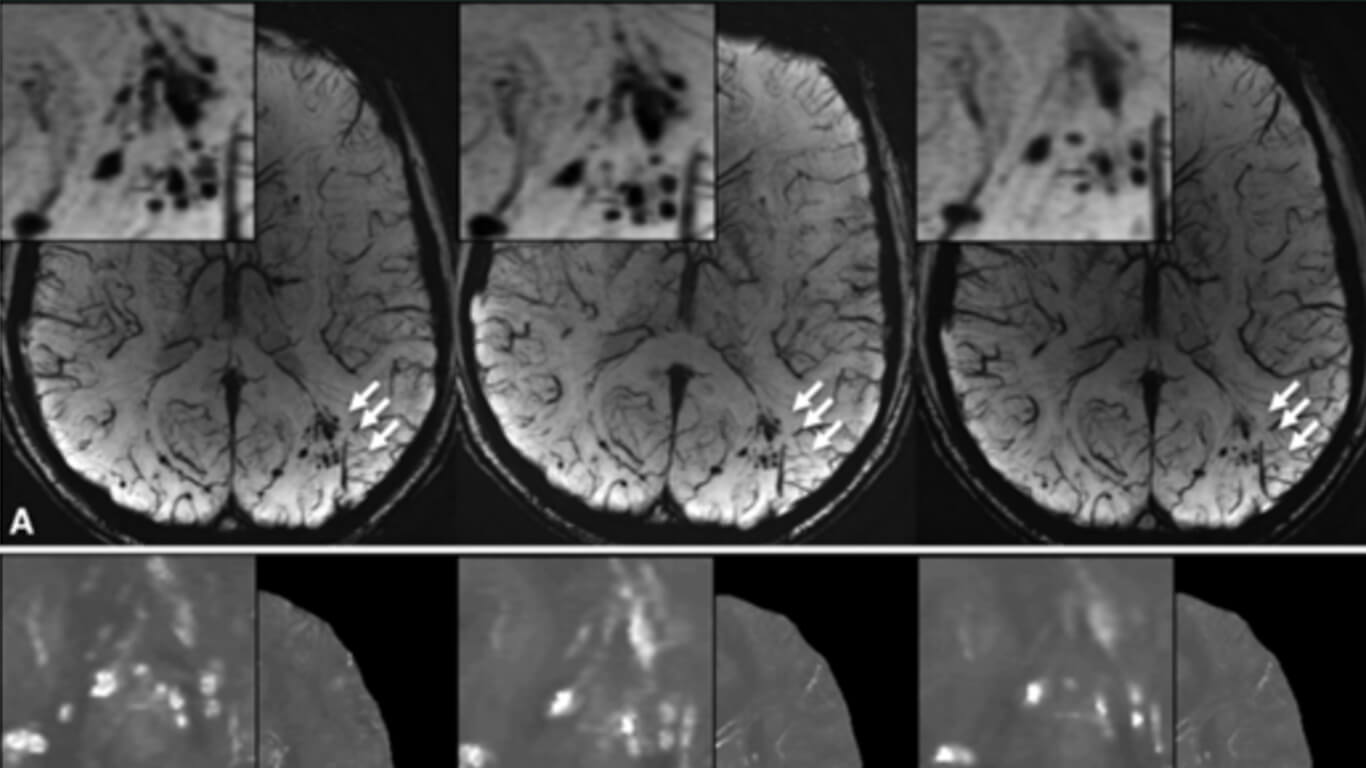
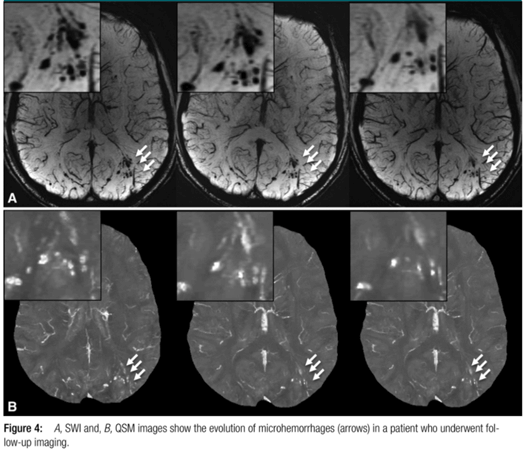
The study was approved by the Walter Reed National Military Medical Center institutional review board and is compliant with HIPAA guidelines. All participants underwent two-dimensional conventional gradient-recalled-echo MR imaging and three-dimensional flow-compensated multiecho gradient-recalled-echo MR imaging (processed to generate susceptibility-weighted images and quantitative susceptibility maps), and a subset of patients underwent follow-up imaging. Microhemorrhages were identified by two radiologists independently. Comparisons of microhemorrhage number, size, and magnetic susceptibility derived from quantitative susceptibility maps between baseline and follow-up imaging examinations were performed by using the paired t test.
Results
Among the 603 patients, cerebral microhemorrhages were identified in 43 patients, with six excluded for further analysis owing to artifacts. Seventy-seven percent (451 of 585) of the microhemorrhages on susceptibility-weighted images had a more conspicuous appearance than on gradient-recalled-echo images. Thirteen of the 37 patients underwent follow-up imaging examinations. In these patients, a smaller number of microhemorrhages were identified at follow-up imaging compared with baseline on quantitative susceptibility maps (mean ± standard deviation, 9.8 microhemorrhages ± 12.8 vs 13.7 microhemorrhages ± 16.6; P = .019). Quantitative susceptibility mapping–derived quantitative measures of microhemorrhages also decreased over time: −0.85 mm3 per day ± 1.59 for total volume (P = .039) and −0.10 parts per billion per day ± 0.14 for mean magnetic susceptibility (P = .016).
Conclusions
The number of microhemorrhages and quantitative susceptibility mapping–derived quantitative measures of microhemorrhages all decreased over time, suggesting that hemosiderin products undergo continued, subtle evolution in the chronic stage.

