Semi-automatic detection of increased susceptibility in multiple sclerosis white matter lesions imaged with 1.5T MRI
By: Karen Holzberger, President & CEO of SpinTech MRI
Author(s): L. Pelizzari a, N. Bergslanda,b, D. Utriainenc,d,e, S. Viotti a, F. Baglioa, L. Mendozzi a, P. Cecconi a, E.M. Haackec,d,f , P. Zamboni g, M.M. Laganàa,∗
Journal: Biomedical Signal Processing and Control
Published: 2020
Read Full Paper: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1746809420301993
Abstract
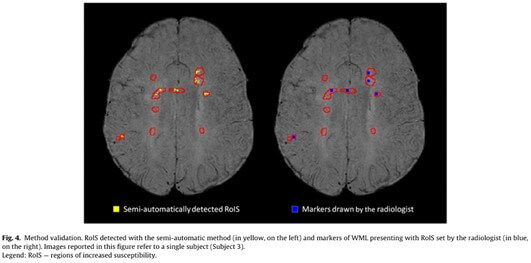
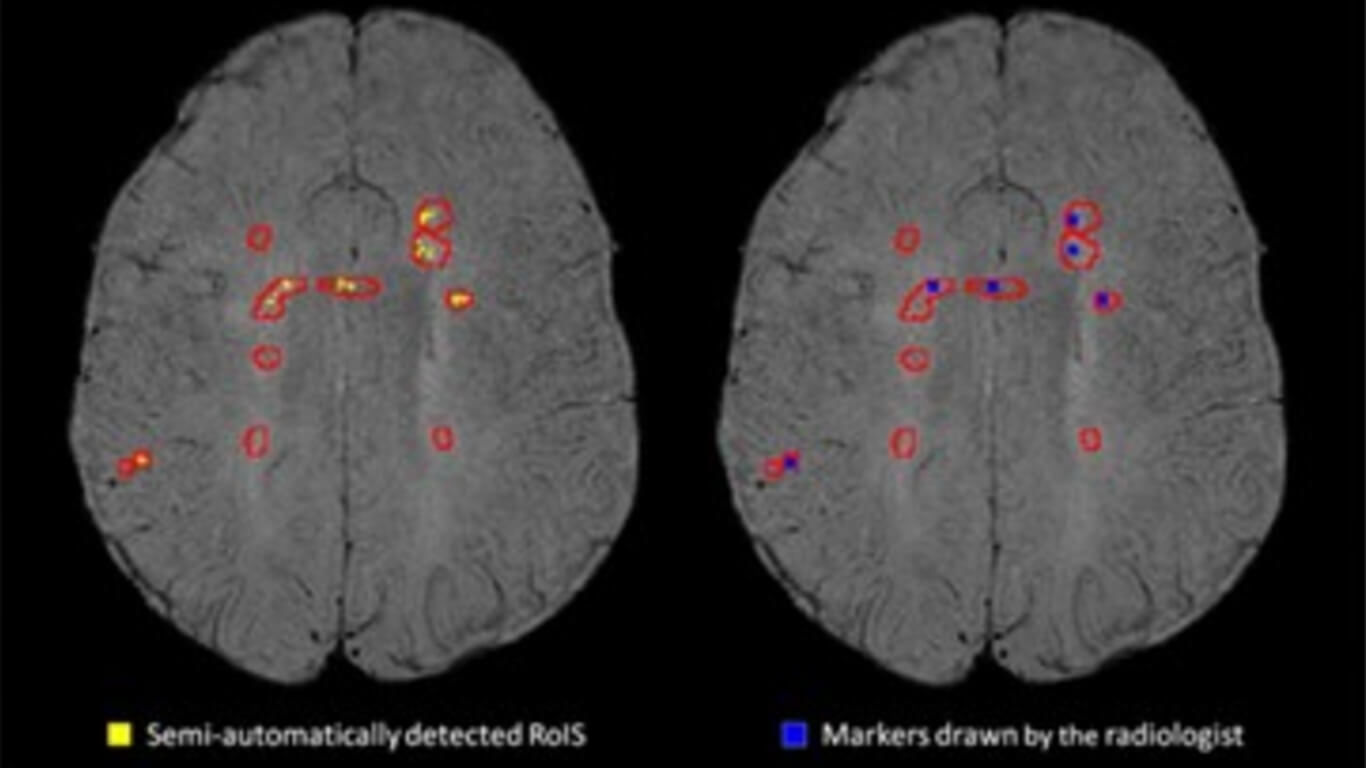
The identification of regions of increased susceptibility (RoIS) in multiple sclerosis (MS) white matter lesions (WML) is currently performed by the radiologist’s visual inspection of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data acquired with high-field MRI scanners. The aims of this study were: 1) to define and validate a semi-automatic method for detecting RoIS in WML from quantitative susceptibility maps (QSM) and susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) acquired with a 1.5 T MRI scanner; 2) to assess the prevalence of WML with RoIS and the susceptibility in those areas; and 3) to test the association between RoIS in WML and clinical outcomes.
Method
Thirty-eight MS patients were scanned on a 1.5 T MRI scanner. T2-hyperintense WML were segmented and superimposed on SWI and QSM images. Two intensity thresholds were defined and consecutively applied for identifying RoIS within WML (thrhyper_QSM to identify QSM hyperintensity within WML and thrhypoSWI to identify SWI hypointensity within WML). The sensitivity and specificity were assessed on a subgroup of subjects. The numbers of WML with RoIS and RoIS volume were determined. Differences between phenotypes and correlations with clinical outcome were tested.
Results
The method showed good sensitivity (95.6%) and specificity (92.1%). On average, 44.7% of the WML showed RoIS, occupying 11.0% of the total lesion volume, with an average susceptibility of 39.4 ± 12.2 ppb. The number of WML with RoIS was negatively correlated with disease duration (r = −0.342, p = 0.035).
Conclusions
The proposed semi-automatic method proved to be suitable for the detection of RoIS in WML at 1.5 T. This approach may be useful in longitudinal studies aiming to monitor susceptibility in WML.

