An interleaved sequence for simultaneous magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) and quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM)
By: Karen Holzberger, President & CEO of SpinTech MRI
Author(s): Yongsheng Chena,b,c , Saifeng Liub , Sagar Buchd , Jiani Hub,c , Yan Kanga , E. Mark Haackea,b,c,d,⁎
Journal: Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Published: 2018
Read Full Paper: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0730725X17302576?via%3Dihub
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to image the entire vasculature of the brain with complete suppression of signal from background tissue using a single 3D excitation interleaved rephased/dephased multi-echo gradient echo sequence. This ensures no loss of signal from fast flow and provides co-registered susceptibility weighted images (SWI) and quantitative susceptibility maps (QSM) from the same scan.
Method
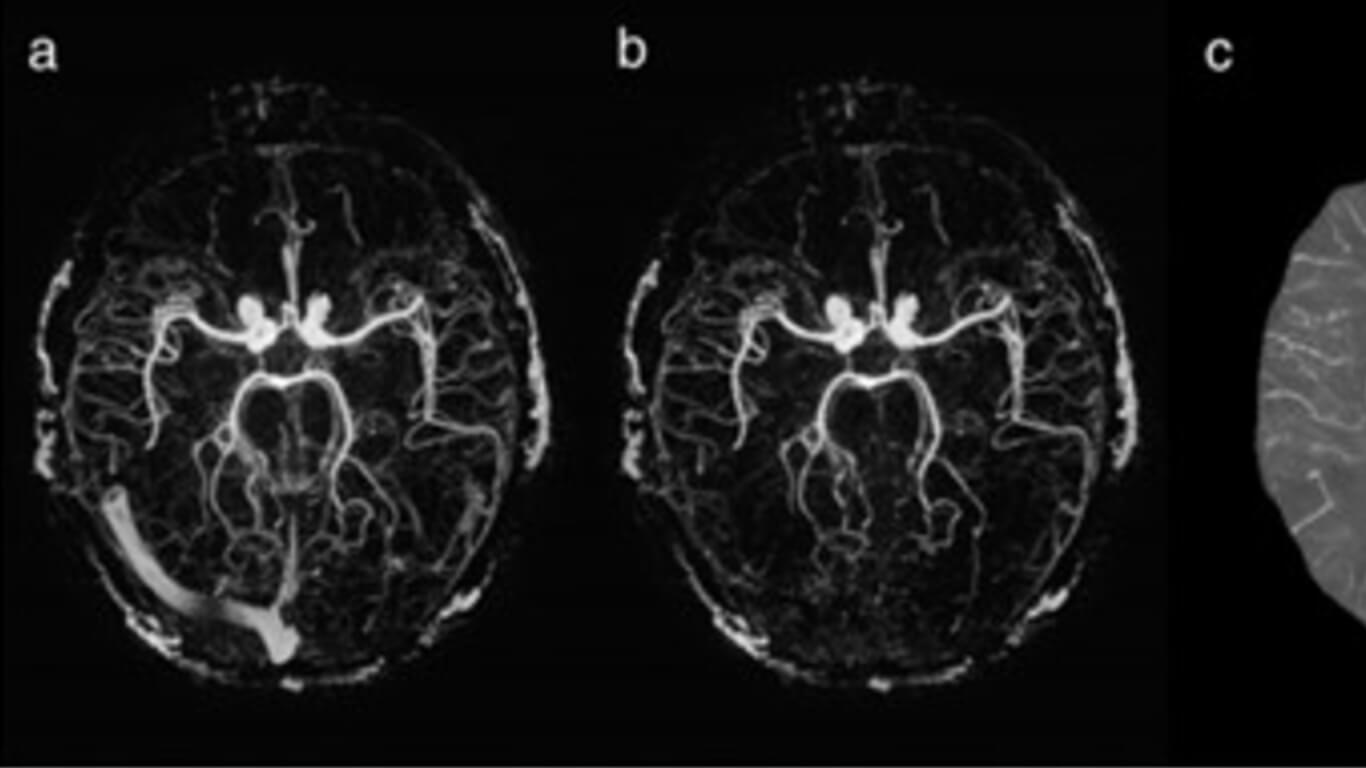
The suppression of background tissue was accomplished by subtracting the flow-dephased images from the flow-rephased images with the same echo time of 12.5 ms to generate a magnetic resonance angiogram and venogram (MRAV). Further, a 2.5 ms flow-compensated echo was added in the rephased portion to provide sufficient signal for major arteries with fast flow. The QSM data from the rephased 12.5 ms echo was used to suppress veins on the MRAV to generate an artery-only MRA. The proposed approach was tested on five healthy volunteers at 3 T.
Results
This three-echo interleaved GRE sequence provided complete background suppression of stationary tissues, while the short echo data gave high signal in the internal carotid and middle cerebral arteries (MCA). The contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) of the arteries was significantly improved in the M3 territory of the MCA compared to the non-linear subtraction MRA and TOF-MRA. Veins were suppressed successfully utilizing the QSM data.
Conclusion
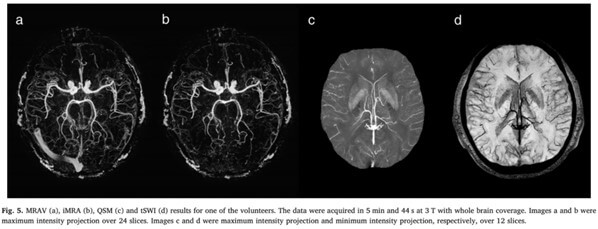
The background tissue can be properly suppressed using the proposed interleaved MRAV sequence. One can obtain whole brain MRAV, MRA, SWI, true-SWI (or tSWI) and QSM data simultaneously from a single scan.

