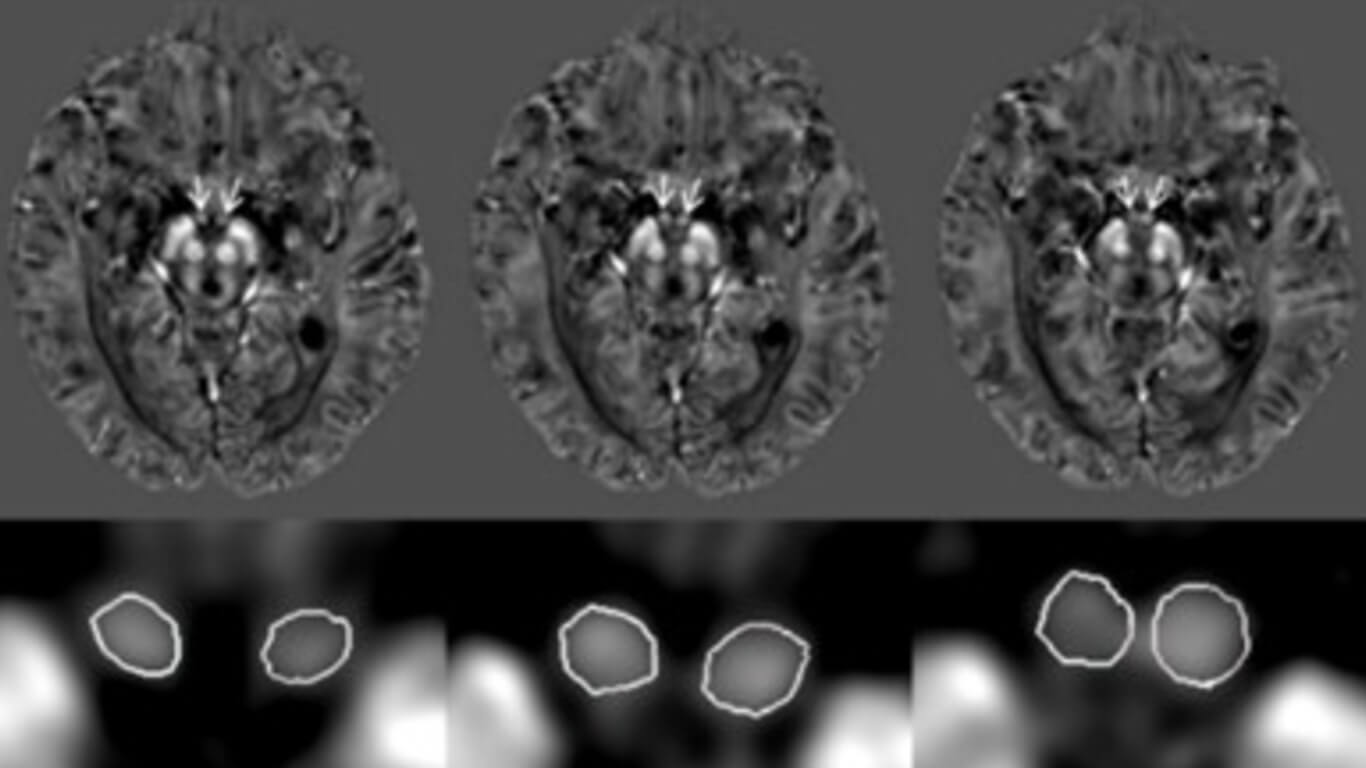
Susceptibility and Volume Measures of the Mammillary Bodies Between Mild Cognitively Impaired Patients and Healthy Controls
By: Karen Holzberger, President & CEO of SpinTech MRI
Author(s): Zhijia Jin1† , Sean K. Sethi2,3† , Binyin Li4 , Rongbiao Tang1 , Yufei Li5 , Charlie Chia-Tsong Hsu6 , Naying He1 *, E. Mark Haacke1,2,3,7 and Fuhua Yan1
Journal: Frontiers in Neuroscience
Published: 2020
Read Full Paper: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnins.2020.572595/full
Abstract
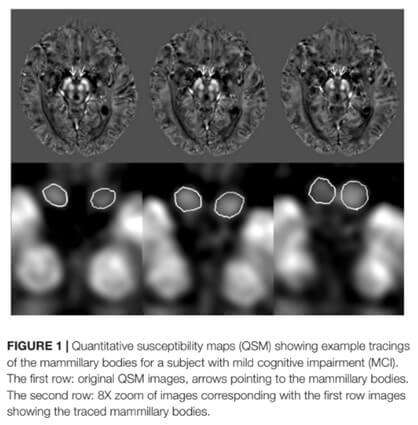
The purpose of this study was to investigate the baseline values and differences for susceptibility and volume of the mammillary bodies between mild cognitively impaired (MCI) patients and healthy controls (HCs), and further explore their differences in relation to gender, MCI subtypes and apolipoprotein E (APOE) genotypes.
Method
T1-weighted and multi-echo gradient echo imaging sequences were acquired on a 3T MR scanner to evaluate the T1W based volume and susceptibility differences in the mammillary body for 47 MCI and 47 HCs. T-tests were performed to compare volume and susceptibility between groups, and right and left hemispheres. Correlation analysis was used to relate the volume and mean susceptibility as a function of age in MCI and HC groups separately, and to investigate the relationship of susceptibility with the neuro-psychological scales in the MCI group.
Results
Susceptibility was found to be elevated within the right mammillary body in MCI patients compared to HCs (p < 0.05). There were no differences for the mammillary body volumes between the MCI and HC groups, although there was a reduction in volume with age for the MCI group (p = 0.007). Women showed decreased mammillary body volume compared to men in the HC group (p = 0.004). No significant differences were found in relation to MCI subtypes and APOE genotypes. No significant correlations were observed between mammillary body susceptibility with neuro-psychological scales.
Conclusions
This work provides a quantitative baseline for both the volume and susceptibility of the mammillary body which can be used for future studies of cognitive impairment patients underlying the pathology of the Papez circuit.

