Quantifying Tissue Properties of the Optic Radiations Using Strategically Acquired Gradient Echo Imaging and Enhancing the Contrast Using Diamagnetic Susceptibility Weighted Imaging
By: Karen Holzberger, President & CEO of SpinTech MRI
Author(s): P.K. Jella, Y. Chen, W. Tu, S. Makam, S. Beckius, E. Hamtaei, C.C.-T. Hsu, and E.M. Haacke
Journal: American Journal of Neuroradiology
Published: 2021
Read Full Paper: http://www.ajnr.org/content/early/2020/12/24/ajnr.A6897
Abstract
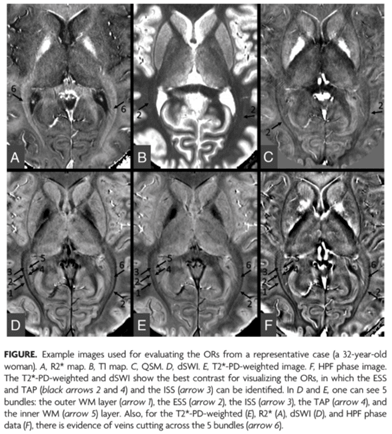
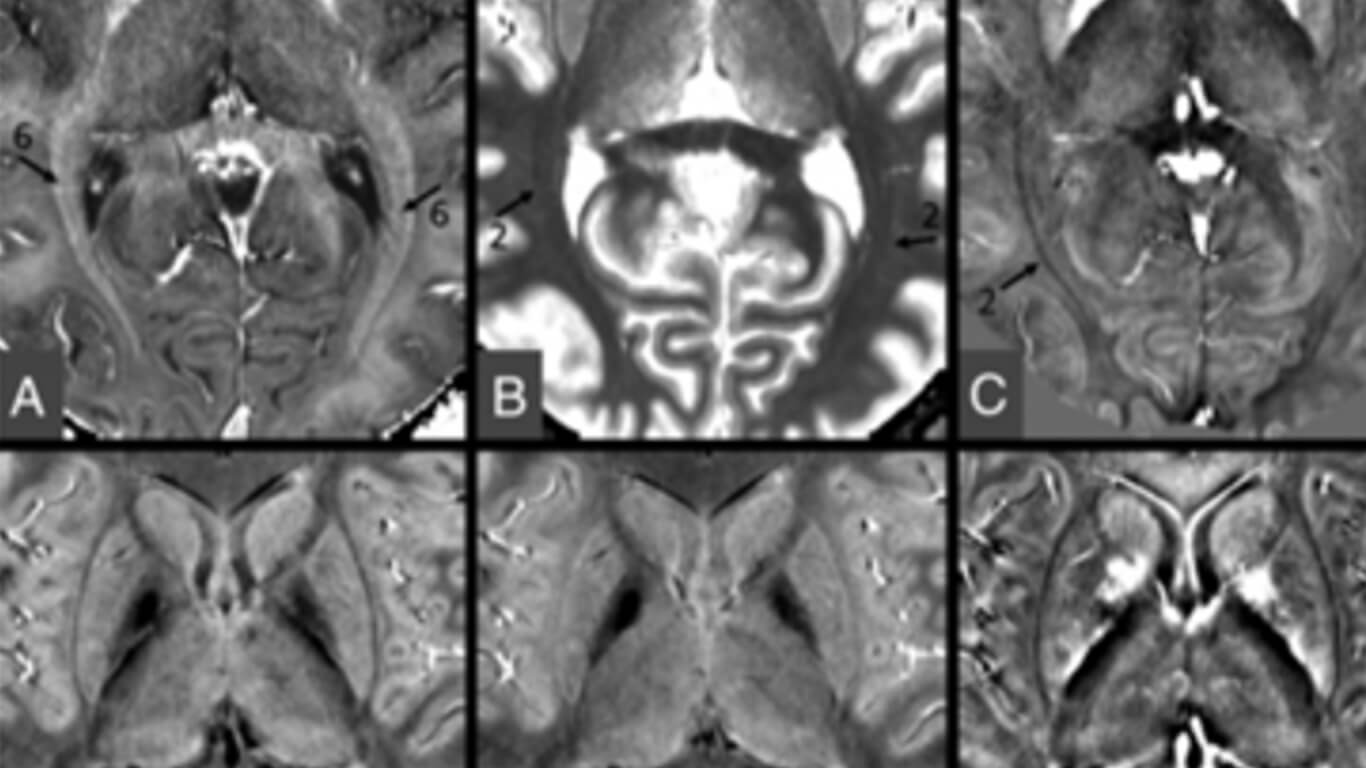
Visualization of the optic radiations is of clinical importance for diagnosing many diseases and depicting their anatomic structures for neurosurgical interventions. In this study, we quantify proton density, T1, T2*, and susceptibility of the optic radiation fiber bundles in a series of 10 healthy control participants using strategically acquired gradient echo imaging.
Furthermore, we introduce a novel means to enhance the contrast of the optic radiations using diamagnetic susceptibility weighted imaging.

